Fossils
are the remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organism.
Permineralized remains
are fossils in which the spaces inside are filled with minerals from groundwater.
Carbon film
A thin film of carbon residue is left, forming a silhuette of the original organism.
Mold
the hard part might decay or dissolve, leaving behind a cavity in the rock.
Cast
a type of body fossil that forms when crystal fill a mold or sediment wash into a mold and harden into rock.
Index fossil
are the remains os species that existed on Earth for relatively short perios of time, were abundant, and were widespread geographically
Principle of superposition
in undisturbed layer of rock, the oldest rocks are on the bottom and the rock become progressively younger towar the top.
Relative age
something is its age in comparison to other things.
Unconformity
The gaps is rock sequences.
Absolute age
is the age, in year, of a rock or other object.
Radioactive decay
the process of braking down energy.
Half-life
time it takes for half the atoms of an isotope to decay.
Radiometric dating
process used to measure de relative age of rock by meassuring the ratio of the parent isotope to daughter product in a mineral and knowing the half-life of the parent.
Uniformitarianism
principle stating that Earth processes ocurring today are similar to those that occurred in the past.
martes, 12 de abril de 2011
miércoles, 6 de abril de 2011
Water erosion and Depositon
Runoff
Water that doesn't soak into the ground or evaporate but instead across Earth's surface
Channel
Water moving down the same path created a grovee
Sheet Erosion
Occurs when water that is flowing as sheet picks up and carries away sediments.
Drainage Basin
Is the area of land fram which a stream or river collects runoff.
Meander
Over time, the curve grows to become a broad arc.
Graundwater
Water that soaks into the ground collects ih these pores and empty spaces
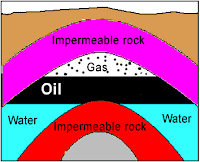
Permeable
Describes soil and rock with connecting pores throught which water can flow
Impermeable
Water cannot pass throught them.
Aquifer
A layer of permeable rock that lets water move freely
Water Table
Upper surface zone of saturation; drops during a drought.
Spring
Form when water table meets Earth's surface; often found in hillsides and used for freshwater source.
Geyser
Hot spring that erupts periodically, shooting water and steam into the ear.
Cave
Underground opening that can form when acidic groundwater dessolves limestone .
Water that doesn't soak into the ground or evaporate but instead across Earth's surface
Channel
Water moving down the same path created a grovee
Sheet Erosion
Occurs when water that is flowing as sheet picks up and carries away sediments.
Drainage Basin
Is the area of land fram which a stream or river collects runoff.
Meander
Over time, the curve grows to become a broad arc.
Graundwater
Water that soaks into the ground collects ih these pores and empty spaces
Permeable
Describes soil and rock with connecting pores throught which water can flow
Impermeable
Water cannot pass throught them.
Aquifer
A layer of permeable rock that lets water move freely
Water Table
Upper surface zone of saturation; drops during a drought.
Spring
Form when water table meets Earth's surface; often found in hillsides and used for freshwater source.
Geyser
Hot spring that erupts periodically, shooting water and steam into the ear.
Cave
Underground opening that can form when acidic groundwater dessolves limestone .
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)